Thermoacoustic Refrigeration
Thermoacoustic refrigeration is a type of
refrigeration in which sound energy is used for creating the cooling effect. Thus
no harmful chemicals are required. Firstly, let us understand what does the
thermoaccoustic means-‘Thermoacoustic’ or thermoacoustics explains the relation between heat and
sound. It is a science that explains how sound energy can be converted to heat
or vice versa, and explains how to realize the conversion practically by means
of special kind of engines and refrigerators.
Now, talking
about refrigeration-it means the removal of heat from cold place and dumping it
to relatively hot place (thereby further cooling the cold place) by means of
some kind of ‘mechanical work.
•
The Principle of REFRIGERATION: The main principle of
refrigeration is to pump heat from lower temperature to higher using work
input. In case of thermoacoustic refrigeration, a high pressure waves are employed for the
required heat transfer. This pressure wave is generated from high frequency
sound wave.
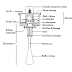
Main
parts of thermoacoustic Refrigerator-
•
Two
main parts
–
Driver
• Houses the Loudspeaker
–
Resonator
• Houses the gas (in this case Helium)
• The hot and cold heat exchangers
• houses
the Stack
Working
of the Thermoacoustic Refrigeration(part by part):
•
Moving
coil Loudspeaker
–
Inside
2 magnets with metal coil between them, current is induced causing coil to move
–
Creates
sound waves up to 200 dB!
•
Resonator—where
gas cooling and compression take place
–
Uses
inert gas, commonly Helium
•
Stack
–
Series
of small parallel channels through which pressure and velocity of waves change
–
In
between the heat exchangers
•
Heat
Exchangers
–
Hot
heat exchanger to remove excess heat
–
Cold
heat exchanger for refrigeration
Advantages
•
Uses
sound for refrigeration –no harmful chemicals (CFC’s, HFC’s, HCFC’s)
•
Few
moving parts—more reliable
•
Not
harmful to the environment
Disadvantages
•
Most
efficient is approaching 40% of Carnot limit
•
20-30%
overall efficiency






0 comments:
Post a Comment